把握機遇:Barnett Rosenberg的抗癌藥物大發現
By Daria Zaitseva

如果不是運氣,有些科學發現就不會發生:蘋果落在牛頓身旁使他想到萬有引力 [1],Roentgen對他實驗室裡神秘發光小屏幕的調查最終使他發現了X射線 [2]。科學史上從不乏偶然遇上的驚喜。本文將介紹另一個無意中的發現,它拯救了無數生命 — 這是Barnett Rosenberg對順鉑(cisplatin)的二次發現。
Rosenberg於1948年從布魯克林學院取得物理學學士學位,並分別於1950和1955年從紐約大學獲得物理學碩士和博士學位 [3]。由於他一直接受物理學訓練,使他能提出生物學家未必能想到的獨特見解:他注意到細胞分裂中的有絲紡綞體看起來就像兩個相反電荷之間的電場線(或兩個相反極性之間的磁場線)(圖一)。這只是巧合嗎?還是電磁學與細胞分裂有關?
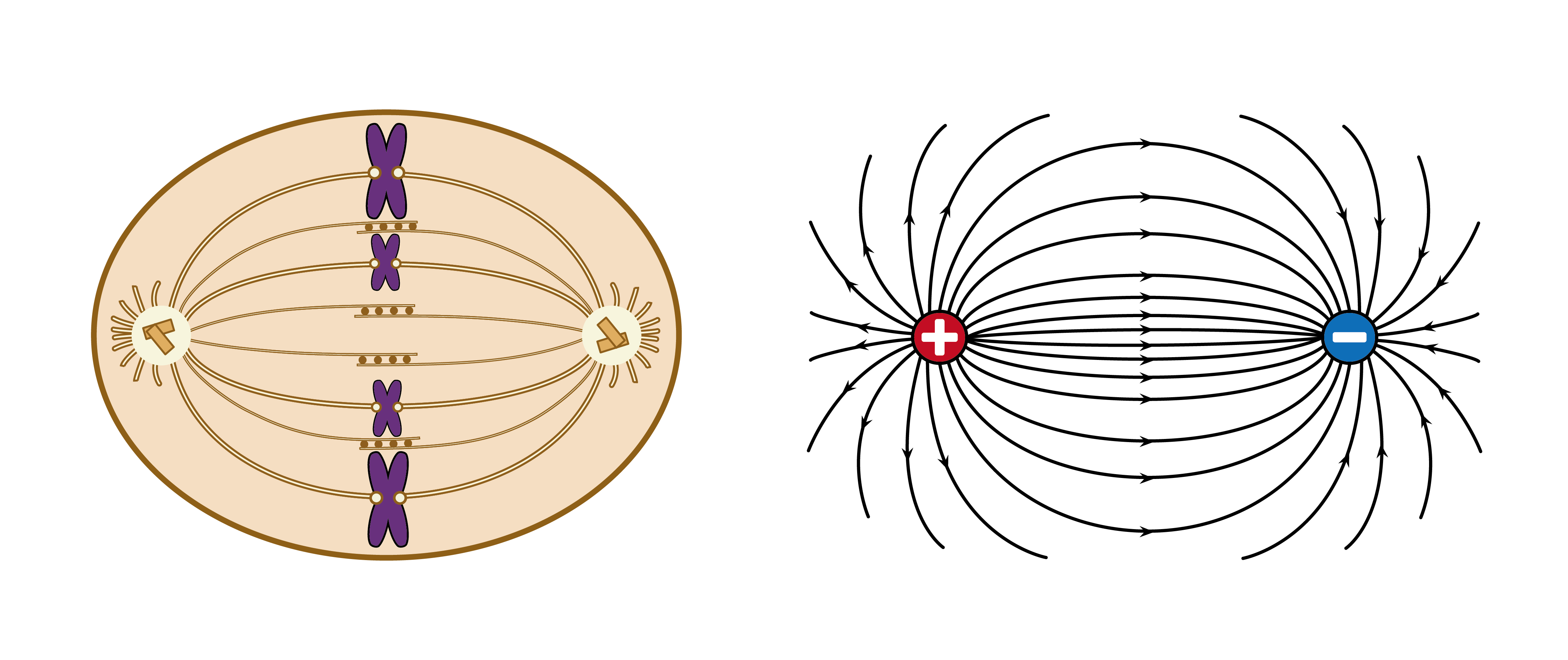
圖一 分裂中的細胞,當中有絲紡綞體與染色體連接(左)和兩個相反電荷之間的電場線(右)
儘管大腸桿菌(Escherichia coli)並不使用有絲紡綞體來進行細胞分裂,Rosenberg還是於1965年在大腸桿菌上試驗了他這個不尋常的想法 [4, 5]。他使用了在生物和化學上也被認為是具惰性的鉑電極,向以氯化銨作為pH緩衝劑的細菌溶液傳送電流 [6]。不管他原來的預測結果是甚麼,他也不會猜到接下來的事情:微生物並沒有分裂得更快;反而,它們全部呈現被拉長,彷彿想分裂但不能成功的樣子。與正常大小相比,它們的長度增加了足足300倍 [7]!因此,Rosenberg認為是電流影響了細胞分裂。
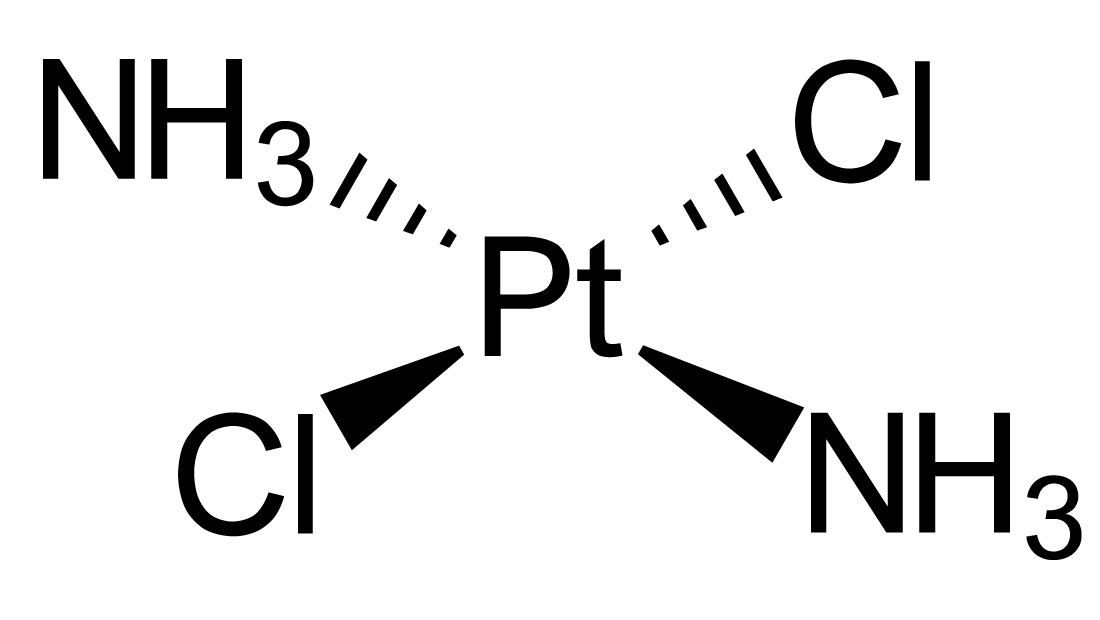
然而,這不是正確的結論。在接下來的兩年,Rosenberg發現阻礙細胞分裂的不是電流,而是在反應中產生的順鉑(圖二)[4, 5]。這種化合物早於1854年已被意大利化學家Michele Peyrone發現,但在Rosenberg二次發現前並沒有人對其作出過深入研究 [4]。與當時許多具有抑制細胞分裂能力的新物質一樣,順鉑被視為化療的候選藥物之一 [4]。
圖二 順鉑的化學結構
1969年,Rosenberg的實驗室發表了有關順鉑在小鼠中具抗腫瘤特性的結果 [3, 8],臨床試驗也隨即展開。起初,它震驚了社會大眾,因為重金屬化合物被認為是具劇毒的物質 [4, 5]。儘管如此,當與其他藥物結合使用時,順鉑對不同類型癌症皆宣告有效,特別是當時沒有有效藥物治療的睾丸癌 [9]。1978年,順鉑被美國食品及藥物管理局(FDA)批准使用,在其他國家也相繼獲得許可 [4]。它至今仍是治療癌症的關鍵藥物之一 [10]。
近年研究揭示了順鉑的運作原理,它主要透過「綁住」(更準確地說是使其形成交聯)同一條DNA鏈上的兩個嘌呤鹼基(腺嘌呤和鳥嘌呤)來抑制DNA複製 [11, 12],最終導致細胞分裂失敗及細胞凋亡 [11]。從順鉑無差別的運作方式來看,它同時亦會影響正常組織中經常需要分裂的細胞,例如腸道內的細胞,引起嚴重副作用 [13]。這在某程度上解釋了為甚麼研究人員在尋找新一代的鉑藥物。對身體毒性較低的卡鉑(carboplatin)在1989年進入市場 [5, 13, 14],對結腸癌尤其有效的奧沙利鉑(oxaliplatin)則在1994年被批准使用 [5, 14]。Rosenberg的偶然發現最終使一系列鉑藥物得以問世,拯救了無數癌症患者的生命。
雖然順鉑的二次發現的確是由許多巧合交織而成,但正是Rosenberg勇於接受新觀點的心態和強烈的好奇心使他能將這重要發現帶給所有人。順鉑的故事亦提醒我們化學、物理和生物之間並沒有實質界限,不同科學領域的緊密合作可以帶來意想不到的重要成果。
機會只留給有準備的人。這是單純的運氣嗎?你自己決定吧。
|
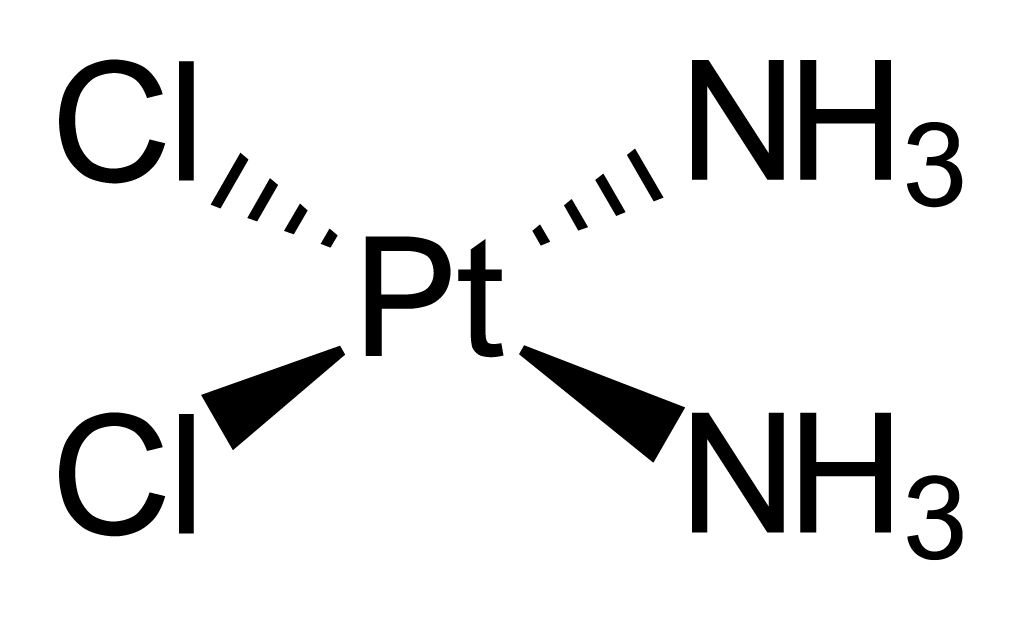
知多一點點:有順鉑,有沒有反鉑(transplatin)? 有,它是順鉑的立體異構體,但沒有抗腫瘤活性 [4]。
反鉑 |
參考資料
[1] Gefter, A. (2010, January 18). Newton's apple: The real story. New Scientist. https://www.newscientist.com/article/2170052-newtons-apple-the-real-story/
[2] This Month in Physics History – November 8, 1895: Roentgen's Discovery of X-Rays. (2001, November). APS News, 10(10), 2.
[3] Hoeschele, J. D. (2014). Biography of Professor Barnett Rosenberg: A Tribute to His Life and His Achievements. Anticancer Research, 34(1), 417–421.
[4] Barnett Rosenberg i ego schastlivyj sluchaj [Barnett Rosenberg and his lucky case]. (2021). Kvantik, 6. https://elementy.ru/nauchno-populyarnaya_biblioteka/436262/Barnett_Rozenberg_i_ego_schastlivyy_sluchay
[5] National Cancer Institute. (2014, May 30). The "Accidental" Cure—Platinum-based Treatment for Cancer: The Discovery of Cisplatin. https://www.cancer.gov/research/progress/discovery/cisplatin
[6] Department of Chemistry, College of Natural Science, Michigan State University. (n.d.). Barney Rosenberg. https://www.chemistry.msu.edu/faculty-research/portraits/rosenberg-barney.aspx
[7] Rosenberg, B., Van Camp, L., & Krigas, T. (1965). Inhibition of Cell Division in Escherichia coli by Electrolysis Products from a Platinum Electrode. Nature, 205(4972), 698–699. https://doi.org/10.1038/205698a0
[8] Rosenberg, B., Van Camp, L., Trosko, J. E., & Mansour, V. H. (1969). Platinum Compounds: a New Class of Potent Antitumour Agents. Nature, 222(5191), 385–386. https://doi.org/10.1038/222385a0
[9] In remembrance of Barnett Rosenberg. (2009). Dalton Transactions, (48), 10648–10650. https://doi.org/10.1039/B918993A
[10] Gandin, V., Hoeschele, J. D., & Margiotta, N. (2023). Special Issue "Cisplatin in Cancer Therapy: Molecular Mechanisms of Action 3.0". International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(9), 7917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24097917
[11] Tchounwou, P. B., Dasari, S., Noubissi, F. K., Ray, P., & Kumar, S. (2021). Advances in Our Understanding of the Molecular Mechanisms of Action of Cisplatin in Cancer Therapy. Journal of Experimental Pharmacology, 13, 303–328. https://doi.org/10.2147/JEP.S267383
[12] Imai, R., Komeda, S., Shimura, M., Tamura, S., Matsuyama, S., Nishimura, K., Rogge, R., Matsunaga, A., Hiratani, I., Takata, H., Uemura, M., Iida, Y., Yoshikawa, Y., Hansen, J. C., Yamauchi, K., Kanemaki, M. T., & Maeshima, K. (2016). Chromatin folding and DNA replication inhibition mediated by a highly antitumor-active tetrazolato-bridged dinuclear platinum(II) complex. Scientific Reports, 6. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24712
[13] Zhang, C., Xu, C., Gao, X., & Yao, Q. (2022). Platinum-based drugs for cancer therapy and anti-tumor strategies. Theranostics, 12(5), 2115–2132. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.69424
[14] Monneret, C. (2011). Platinum anticancer drugs. From serendipity to rational design. Annales Pharmaceutiques Françaises, 69(6), 286–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharma.2011.10.001